728x90
SMALL
이해
수학 문제다. Josephus problem은 wiki에도 잘 나와있다.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Josephus_problem
Josephus problem - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to navigation Jump to search In computer science and mathematics, the Josephus problem (or Josephus permutation) is a theoretical problem related to a certain counting-out game. A drawing for the Josephus problem
en.wikipedia.org
1에서 인덱스가 시작하면, 총 n명일 때 s에 있던 사람이 옮겨지면서 ((s-1){mod {n}})+1} 의 위치로 간다.
f(n,k)이 생존자의 자리라고 하자. k번째 사람이 죽으면, n-1개가 원안에 남는다.
다시 시작되는 카운트(원을 순환)는 k mod {n} + 1 자리에 있던 사람부터 시작한다.
남은 원 안에 남은 생존자의 자리는 f(n-1,k)가 될 것이다.
따라서 다음의 점화식이 나온다.
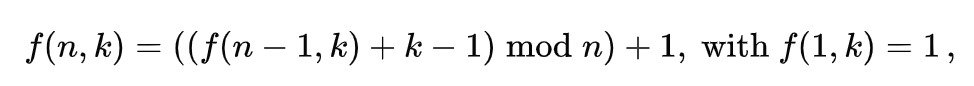
시행착오

메모리가 아주 작다
그것도 모르고... 재귀에 메모이제이션까지 열심히 썼던 나
틀린 코드이다.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int MAX = 5000001;
int memo[MAX];
int josephus(int n, int k) {
if (n==1) {
return 1;
}
if (memo[n] == 0) {
memo[n] = (josephus(n-1, k) + k-1) % n + 1;
}
return memo[n];
}
int main(void) {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n,k;
cin >> n >> k;
cout << josephus(n, k);
return 0;
}
이대로 내면 메모리 초과 받는다.
코드
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int MAX = 5000001;
int main(void) {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int n,k;
cin >> n >> k;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // f(n,k)=((f(n-1,k)+k-1)mod n)+1, with f(1,k)=1
ans = (ans + k - 1) % i + 1;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
출처
728x90
LIST
'PS > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| H대학의 'ㄹ고리즘 분석' 수강생들을 위한 백준 문제 (추가 중) (3) | 2021.10.13 |
|---|---|
| 백준 11049 (C++) 행렬 곱셈 순서 (0) | 2021.10.13 |
| 백준 17498 (C++) 폴짝 게임 (2) | 2021.10.06 |
| 백준 17398 (C++) 통신망 분할 (3) | 2021.10.04 |
| 백준 14938 (C++) 서강그라운드 (0) | 2021.09.30 |